Understanding the Galvanization Process of Telecom Towers
Maximizing Durability and Corrosion Protections
The galvanization process is a vital part of manufacturing telecom towers, ensuring long-term protection against harsh environmental conditions. Steel towers, especially in the telecommunications industry, face constant exposure to weather, moisture, and other corrosive elements. To prevent structural degradation and extend their service life, galvanizing the steel is essential. This process enhances the durability of telecom towers, reduces maintenance costs, and complies with international standards.
The Importance of Galvanic Protection
Galvanic protection is a method that shields steel towers from rust and corrosion. It involves coating the surface with a protective layer of zinc through galvanization, creating a barrier that prevents harmful reactions between the steel and environmental factors. Zinc acts as a sacrificial metal, corroding before the steel itself, ensuring long-lasting protection.
Telecom towers often serve critical infrastructure functions, and corrosion can lead to failure or even collapse if not properly mitigated. Galvanic protection offers a practical solution, protecting against galvanic corrosion—a process that occurs when two dissimilar metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte. Since steel is prone to rust when expose to moisture, this protection is crucial in outdoor telecom installations.

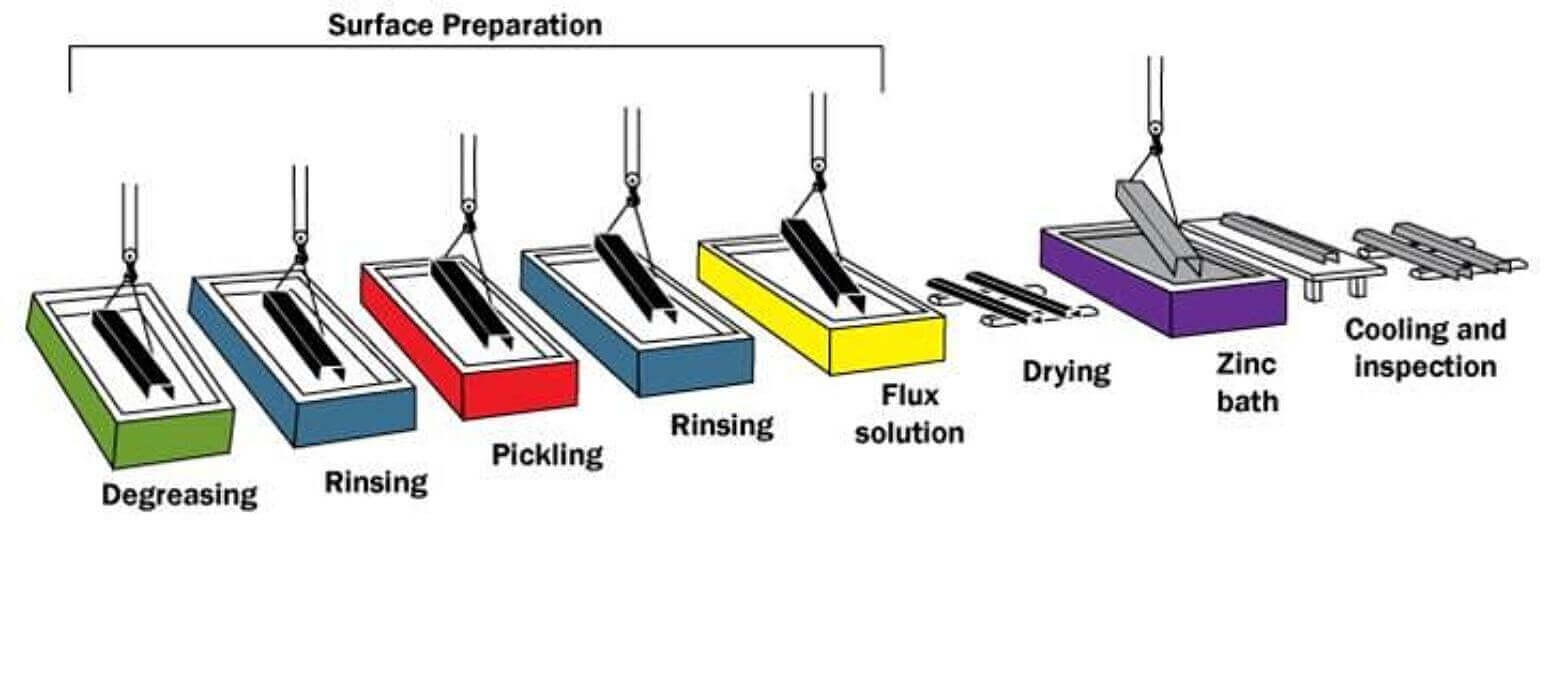
How Galvanization Maximizes the Lifespan of Telecom Towers
Galvanizing your telecom towers increases their lifespan significantly. During the galvanization process, steel components are dipped in molten zinc, forming a metallurgical bond. This zinc coating shields the steel from exposure to corrosive elements such as rain, salt, and pollution. In regions with harsh climates or heavy industrial activity, the towers need extra protection, which galvanization provides.
The coating also serves as a secondary layer of protection. Even if the zinc layer gets damage, it corrodes at a slower rate than steel. This self-healing property ensures long-term structural integrity, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
Understanding Galvanic Corrosion and Its Prevention
Galvanic corrosion occurs when two different metals are in contact with each other and an electrolyte. To prevent this on steel telecom towers, galvanization creates a uniform zinc layer. This zinc layer corrodes instead of the steel, offering sacrificial protection.
Preventing galvanic corrosion also requires using high-quality connections and bolts that are similarly treated or coated to avoid reactions between dissimilar metals. By ensuring compatibility among materials, tower integrity is maintained over the long term.
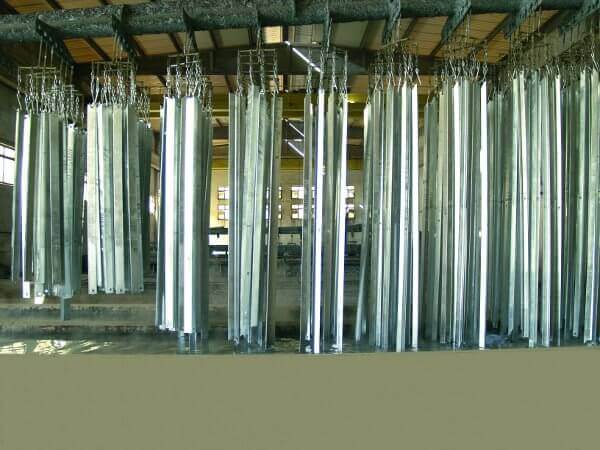
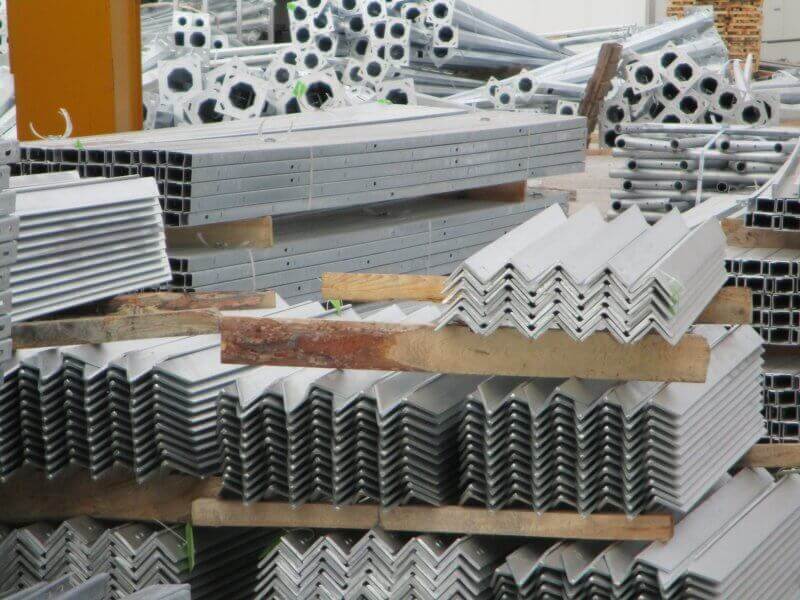


Methods of Protection for Steel Towers
In addition to galvanization, there are other ways to protect steel telecom towers from corrosion. One of these is applying protective coatings, such as paint or powder coatings, which can be layered over the galvanized surface. Another method includes using corrosion inhibitors and installing tower components in environments with controlled humidity levels.
However, the most effective long-term protection remains the galvanization process. It requires little maintenance compared to other methods, making it cost-effective for tower owners and operators. The durability of a well-galvanized telecom tower ensures it will stand strong for decades, often without needing major repairs.
International Standards for Galvanization of Telecom Towers
Galvanizing steel telecom towers must comply with strict international standards to ensure consistent quality and protection. The most common standards include:
- ISO 1461: This standard specifies the requirements for hot-dip galvanized coatings on fabricated iron and steel articles. It ensures uniform coating thickness and quality.
- ASTM A123: An American standard that defines specifications for zinc coatings on iron and steel products.
- EN 1090: A European standard that includes specifications for the execution of steel structures, including surface protection methods like galvanization.
These international standards ensure that the towers meet quality benchmarks and are prepared for various environmental challenges.
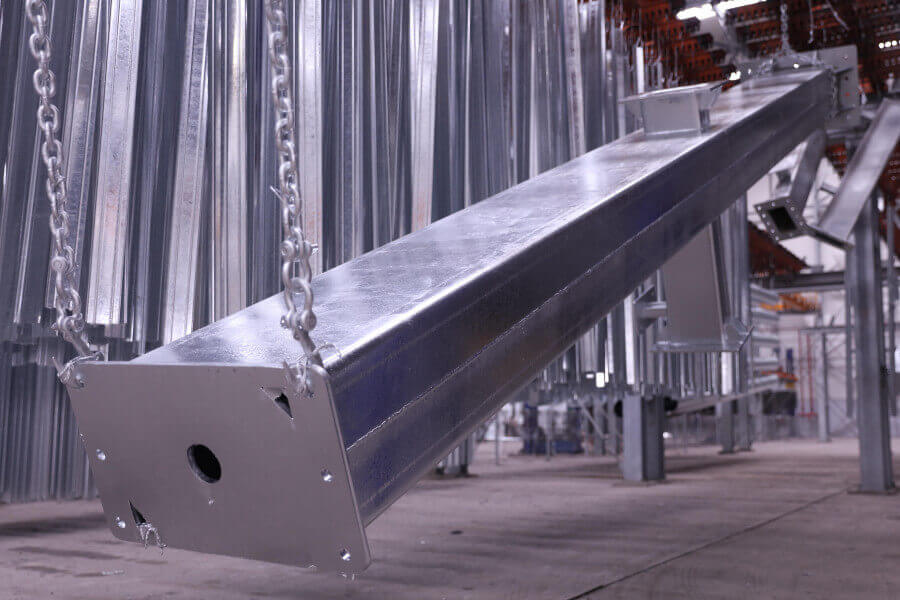


Conclusion
Galvanization plays a critical role in ensuring the durability and longevity of telecom towers. The process not only protects against corrosion but also adheres to international standards that guarantee safety and reliability. With galvanic protection in place, telecom towers can operate in even the most demanding environments without compromising performance. As the telecommunications industry continues to expand, choosing the right corrosion protection method, like galvanization, is key to reducing long-term costs and maintaining operational integrity.
[…] as a tall structure designed to support antennas and other telecommunications equipment. Also these towers are strategically place on to provide wireless connectivity over specific geographical areas, known […]