Bolts, Nuts and Washers for Steel Towers
Transmission Line Towers Connection Elements
Connection elements like bolts, nuts, and washers are essential for energy transmission lines. These components must provide strong mechanical bonds while ensuring electrical continuity. High-strength, corrosion-resistant materials, such as galvanized steel or stainless steel, are commonly used to withstand environmental exposure and prevent rust.
Proper torque application is crucial when tightening bolts and nuts. It ensures a firm connection and avoids over-tightening, which can damage the components or cause failure. Washers distribute the load and reduce wear, helping to maintain the integrity of the joint.
Good contact between elements ensures low electrical resistance. Poor connections can lead to energy loss and overheating, posing safety risks. Regular inspections should check for signs of wear or corrosion, and any issues must be address promptly to prevent failure.
Finally, compliance with industry standards is necessary to guarantee safety and reliability in energy transmission systems.
Methods for Properly Torquing Bolts
Bolts can be torqued using various methods to ensure they are tightened to the correct specifications:
- Torque Wrench: This tool applies a specific amount of torque to the bolt, ensuring proper tension without over-tightening. The wrench can be mechanical, digital, or beam-type, depending on the precision required.
- Hydraulic Torque Wrench: Used for larger bolts, this wrench operates with hydraulic pressure to apply high levels of torque, often necessary in energy transmission lines.
- Pneumatic Torque Wrench: Powered by compressed air, this tool is ideal for repetitive tightening of bolts and provides consistent torque.
- Turn-of-Nut Method: This method tightens the bolt until it reaches a snug condition, then rotates it a specific fraction of a turn to achieve the desired tension. It’s common in construction for larger bolts.
- Torque Multipliers: These devices increase the torque applied by a standard wrench, useful for high-torque applications where space is limited.
- Ultrasonic Torque Measurement: This advanced technique uses sound waves to measure bolt stretch and apply the correct torque indirectly, ensuring accuracy, especially in critical applications.
Lastly each method ensures the correct tension and clamping force, preventing under- or over-tightening, which could lead to connection failure.
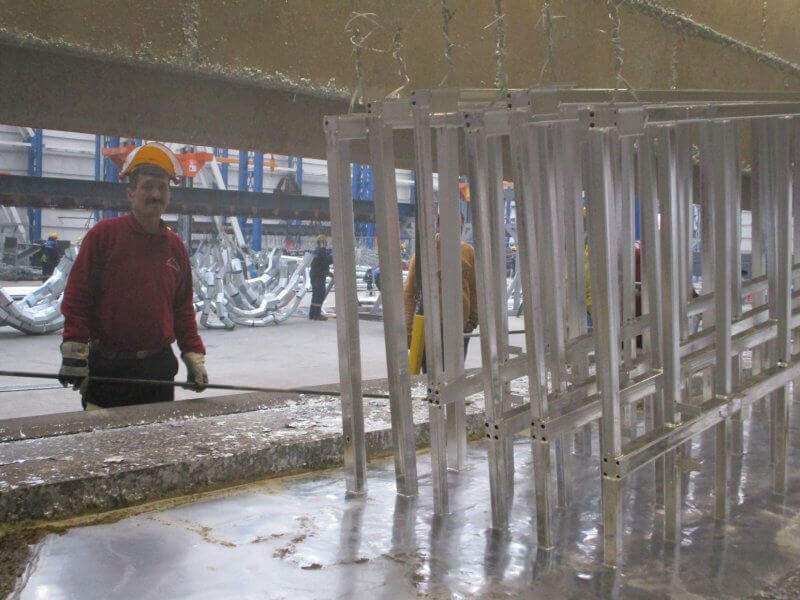


Galvanization of Bolts, Nuts, and Washers
Galvanization is a process used to coat bolts, nuts, and washers with a layer of zinc to prevent corrosion. This coating acts as a barrier, protecting the metal from moisture and harsh environmental conditions.
In conclusion There are two common methods: hot-dip galvanizing and electro-galvanizing. In hot-dip galvanizing, the components are dipped in molten zinc, which forms a thick, durable layer.
However Electro-galvanizing involves a thinner coating applied through an electric current. Both methods provide excellent protection, but hot-dip is more suitable for outdoor and industrial use due to its thicker coating.
On the other hand proper galvanization extends the lifespan of the connection elements, making them more reliable in energy transmission systems.
International Quality Standards for Galvanization of Bolts, Nuts, and Washers
The international quality standards for galvanization of bolts, nuts, and washers are defined by several organizations to ensure durability, corrosion resistance, and performance. Some key standards include:
- ISO 1461: Firstly This standard covers the requirements for hot-dip galvanized coatings on fabricated iron and steel articles. It specifies coating thickness, adhesion, and appearance to ensure reliable protection.
- ISO 4042: This standard deals with electroplated coatings, including zinc coatings applied to fasteners such as bolts and nuts. It focuses on corrosion protection and coating thickness.
- ASTM A153/A153M: Widely use in the United States, this standard specifies requirements for zinc coatings (hot-dip) on iron and steel hardware, including bolts, nuts, and washers.
- ASTM B633: This standard outlines the requirements for electrodeposited zinc coatings on iron and steel, with specific criteria for corrosion resistance and coating thickness.
- EN ISO 10684: This European standard applies to hot-dip galvanized coatings on threaded fasteners and specifies minimum coating thicknesses to ensure adequate corrosion protection.
Also these standards ensure that the galvanization process provides the necessary protection for components used in energy transmission lines and other applications.


Manufacturing Standards of Bolts, Nuts, Washers
The manufacturing standards for bolts, nuts, and washers are established by international organizations to ensure quality, durability, and compatibility in various industrial applications. Some key standards include:
- ISO 898-1: This standard specifies the mechanical properties of steel bolts, screws, and studs. It defines performance grades, tensile strength, and yield limits for fasteners.
- ISO 4032: This standard outlines the dimensional requirements for hexagon nuts, including tolerances, thread types, and sizes. It ensures nuts fit properly with matching bolts.
- ISO 7089: This is the standard for plain washers. It specifies dimensions, material requirements, and surface finishes for washers to ensure even load distribution and minimize wear.
- ISO 4759-1: This standard sets dimensional tolerances for bolts, screws, nuts, and washers, ensuring precise manufacturing and interchangeability between parts.
- ASTM A307: Commonly use in the U.S., this standard covers carbon steel bolts and studs with specified tensile properties. Also ASTM A307 use in a range of applications, including general-purpose construction.
- DIN 933: This German standard specifies hexagon head bolts with metric threads, ensuring consistent sizing and performance.
- ASME B18.2.1: This American standard covers the dimensions and tolerances for hexagon head bolts, screws, and nuts. It ensures these fasteners are reliable and meet industry demands.
Furthermore these standards guarantee the consistent production of bolts, nuts, and washers, ensuring they meet specific mechanical and dimensional requirements for various industrial uses, including energy transmission.
In conclusion, adhering to international manufacturing standards is crucial for producing reliable bolts, nuts, and washers. Also these standards ensure that fasteners meet specific requirements for mechanical properties, dimensions, and corrosion resistance. By following guidelines from organizations like ISO, ASTM, DIN, and ASME, manufacturers can deliver high-quality components that perform consistently across various applications.