Understanding Guy Wire Turnbuckles: Function, Benefits, and Applications for Guyed Masts
What Are Guy Wire Turnbuckles?
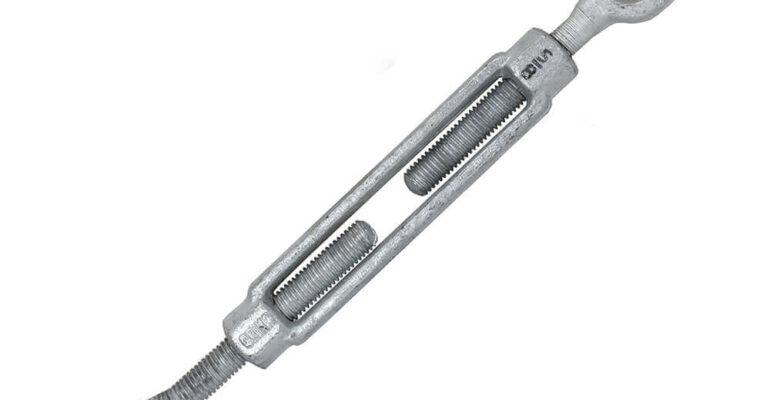
Guy wire turnbuckles are adjustable metal devices which has design to tension and secure guy wires on structures. These structures like masts, towers, and antennas. By tightening or loosening the guy wires, turnbuckles help keep structures stable, aligned. Also they keep secure under various loads, including wind or other environmental factors. Typically made from strong materials like stainless steel or galvanized metal, turnbuckles are essential components in construction and rigging.
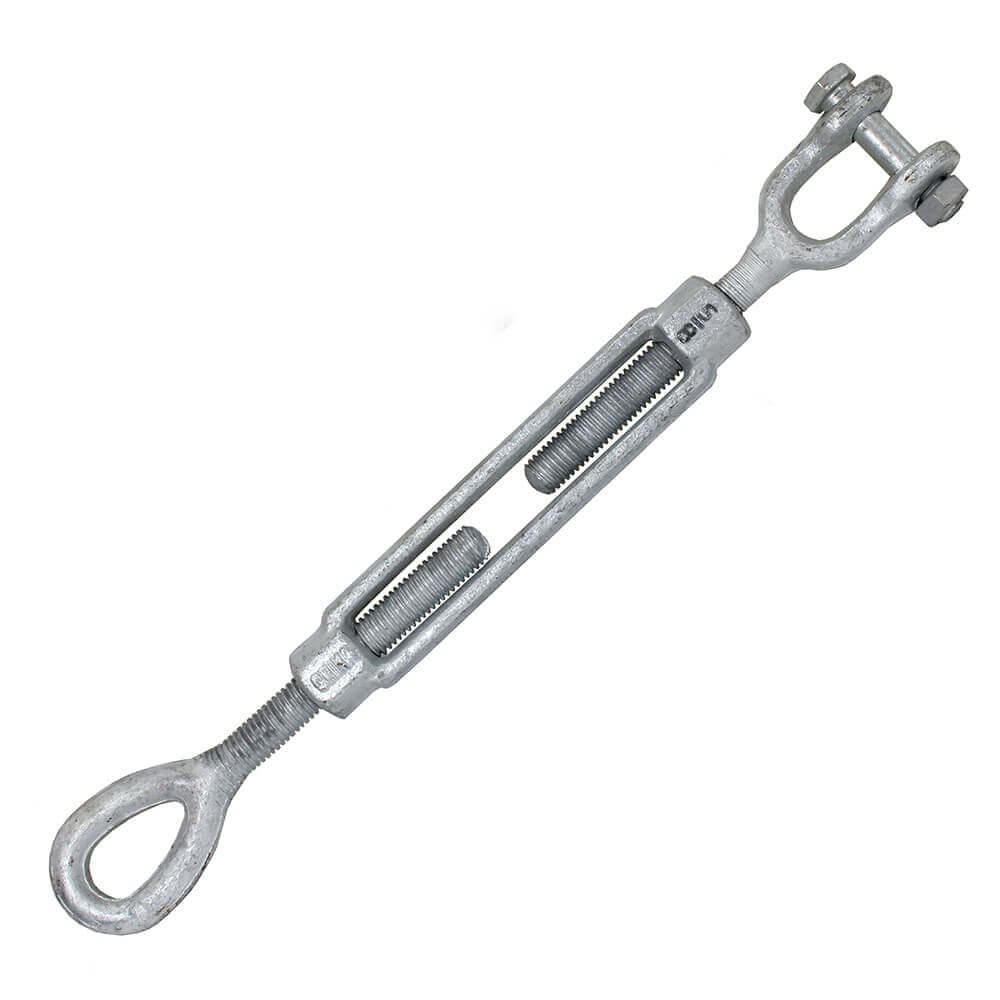


How Do Turnbuckles Work?
Turnbuckles operate through a straightforward mechanism. They consist of a metal body with two threaded ends, each attached to hooks, eyes, or jaws. As you twist the body, the threads move the ends closer together or farther apart, depending on the direction of rotation. This simple action allows you to either increase or decrease tension in the attached guy wires. Also this creating a secure and adjustable hold.
To adjust a turnbuckle, you start by loosening or tightening it with a wrench or by hand. Turning the body clockwise pulls the ends closer, creating more tension on the guy wire. Conversely, turning it counterclockwise reduces tension, which is useful for adjustments during installation or maintenance.
What Are Guyed Mast Anchors?
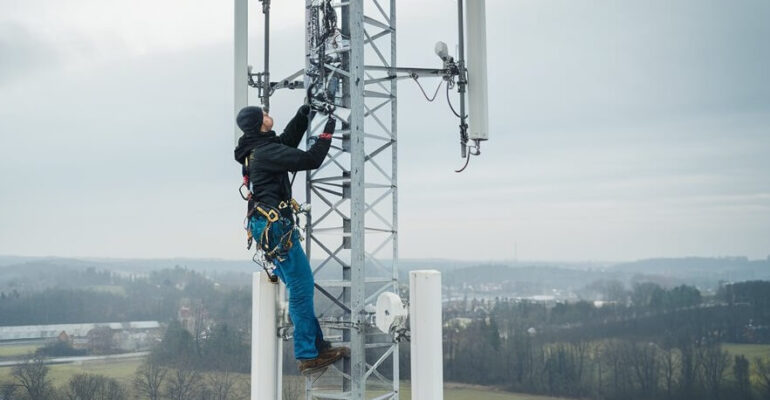
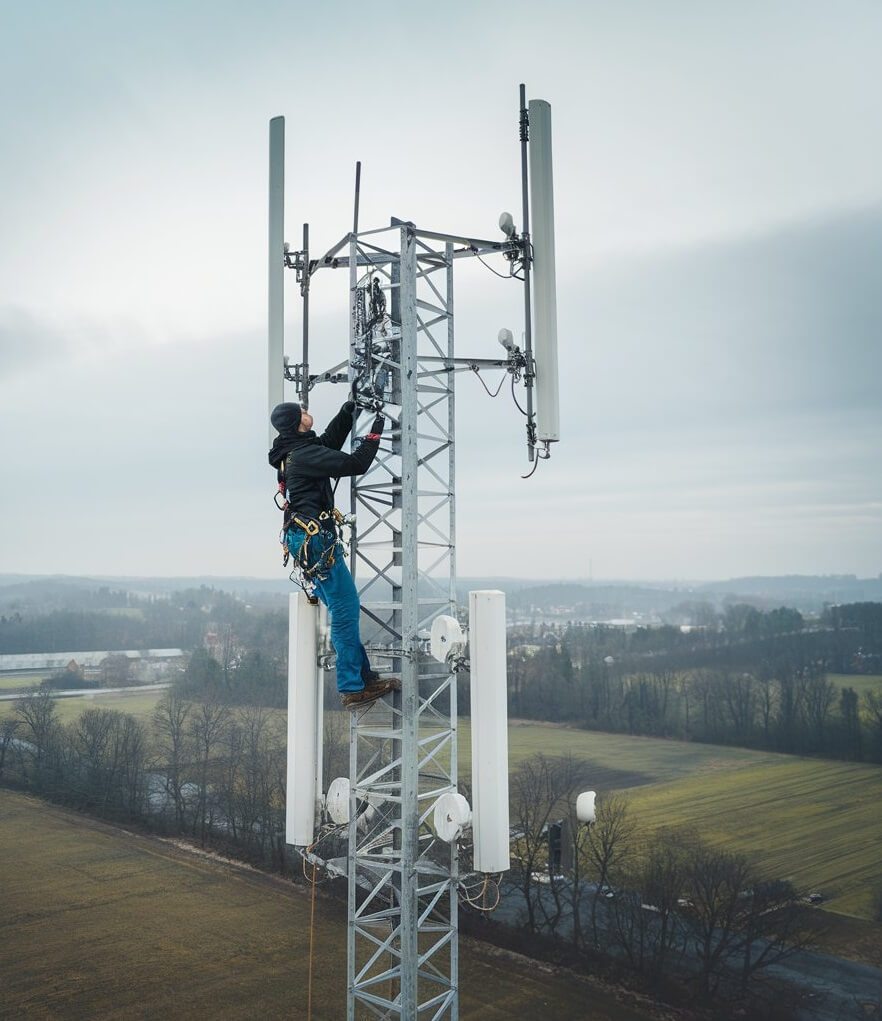
Guyed mast anchors are crucial support elements used to secure the guy wires that stabilize and balance guyed masts, which are tall, slender structures commonly used in telecommunications, broadcasting, and other industries. These anchors are embedded into the ground around the base of the mast, providing a solid attachment point for the guy wires that keep the mast upright, even in harsh weather conditions.
Types of Guyed Mast Anchors
Guyed mast anchors come in several types, each suited to different soil conditions, load requirements, and project specifications:
- Screw Anchors: These are helical, screw-like anchors that are twisted into the ground, providing a strong hold, especially in softer soils. Their shape offers high resistance against pullout forces, making them reliable for masts in areas prone to wind or ice loading.
- Grouted Anchors: Grouted anchors are installed in drilled holes filled with a bonding material, like grout or concrete. These anchors are highly effective in rocky or dense soil types where other anchors may struggle for stability.
- Deadman Anchors: Consisting of a large buried object, often a concrete block or steel plate, deadman anchors use weight and soil friction to hold the mast’s guy wires. They are generally used in areas where other anchors are difficult to install.
- Driven Rod Anchors: These anchors are long rods that are driven directly into the ground. Suitable for a variety of soil conditions, they work well in situations where quick installation is necessary, though they may require deeper installation for heavy load-bearing applications.
Why Are Turnbuckles So Useful?
Turnbuckle offer several advantages that make them invaluable in securing guyed structures:
- Precise Tension Control: With turnbuckles, you can make fine adjustments to wire tension, allowing for precise control that keeps the structure steady.
- Easy Adjustments: Turnbuckles are easy to adjust. Moreover they are enabling quick changes when tightening or loosening wires to handle wind, vibrations, or other loads.
- Durability: Made from corrosion-resistant materials, turnbuckles endure harsh environmental conditions, which enhances the longevity of guyed masts and towers.
- Versatility: Turnbuckles come in various sizes and configurations, making them suitable for a wide range of guyed structures.

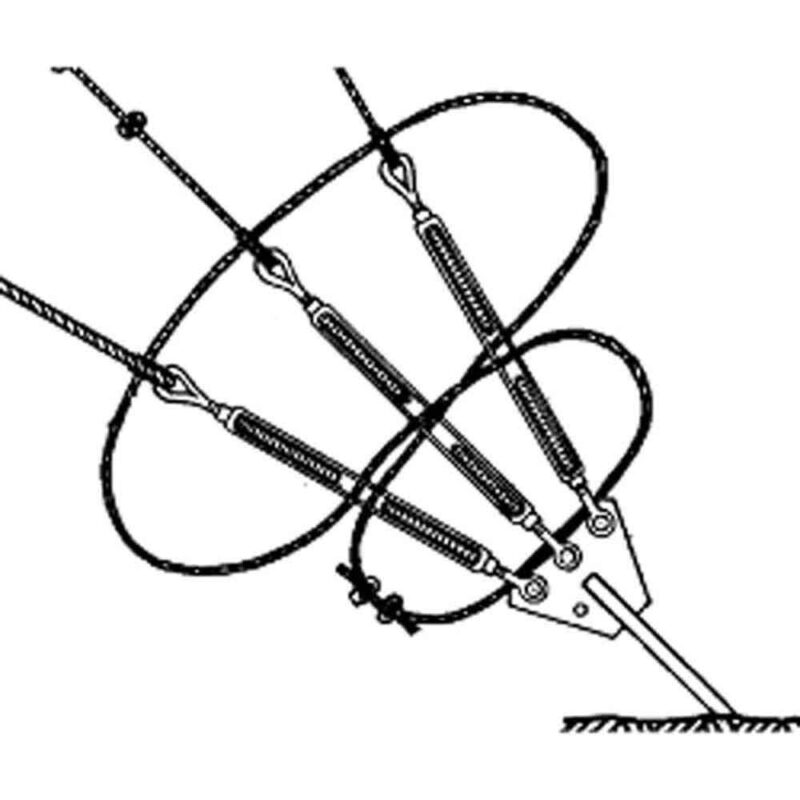
How to Use Turnbuckles on a Guyed Mast
When setting up guy wires on a guyed mast, turnbuckles play a central role. Especially in adjusting and securing the wires for maximum stability. First, you attach the turnbuckles to anchor points on the mast and secure them to each guy wire. Then, you use the turnbuckles to fine-tune the tension of each wire, ensuring even distribution around the mast.
Regularly inspect and adjust turnbuckles as needed. Especially in environments with shifting loads due to wind or ice. This routine maintenance helps prevent slack or over-tightening. Therefore this can destabilize the mast or even cause structural issues.
Conclusion
In summary, guy wire turnbuckles are essential tools for safely securing and stabilizing guyed masts. Their straightforward, adjustable design allows for precise tension control. Also enhancing both the stability and durability of towers and masts in demanding environments.